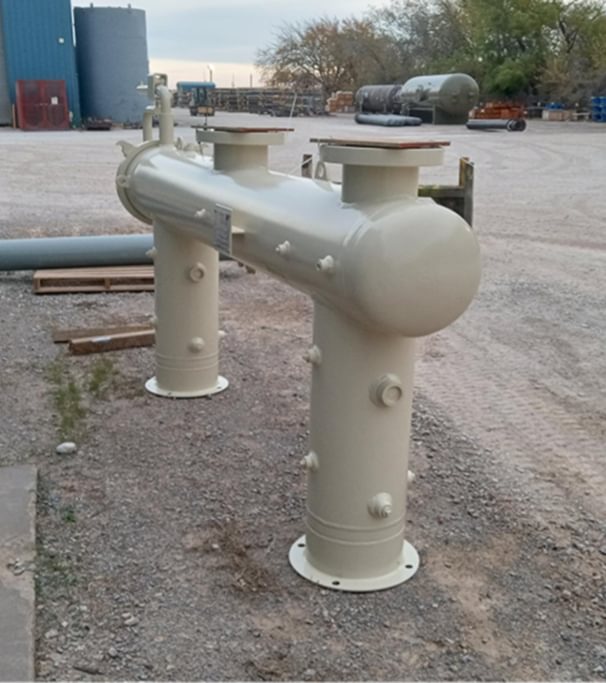
Models
-
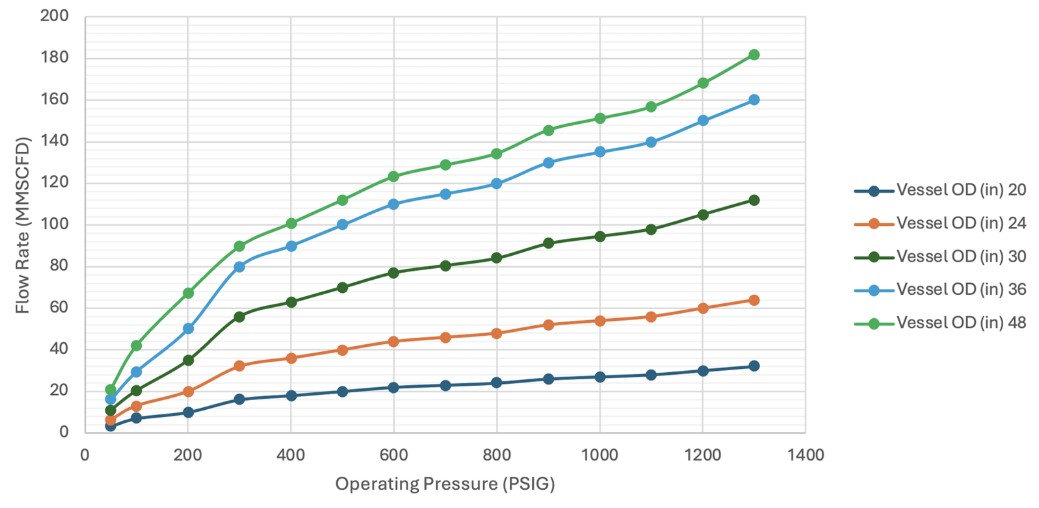
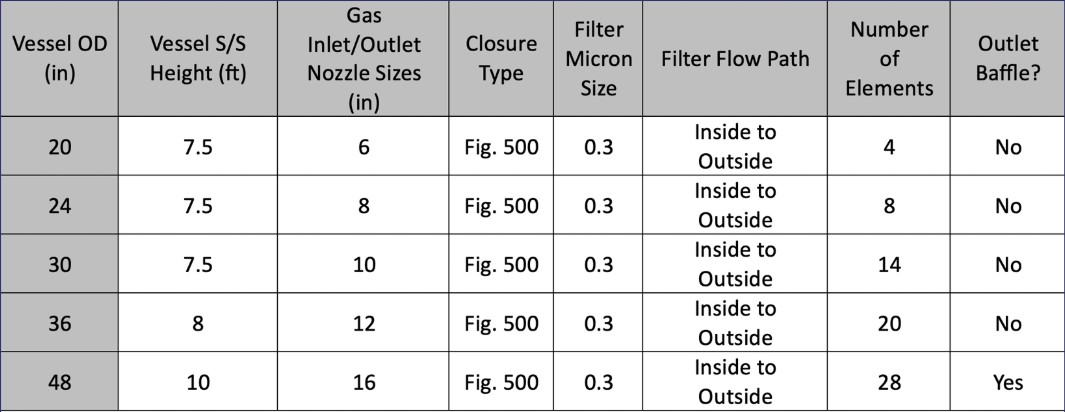
Vertical Coalescers
- Standard sizes up to 54”ID+, 200MMSCFD+
- Custom designs
-
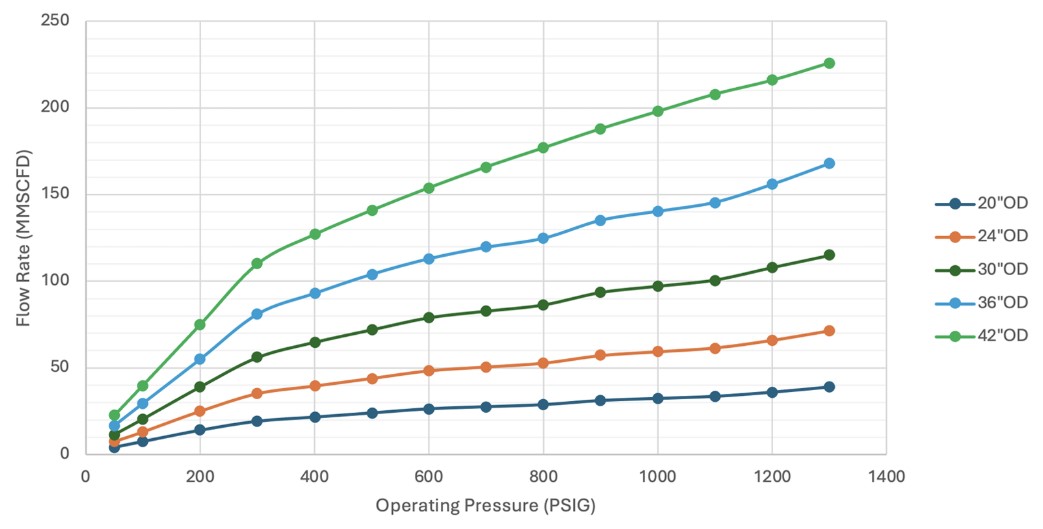
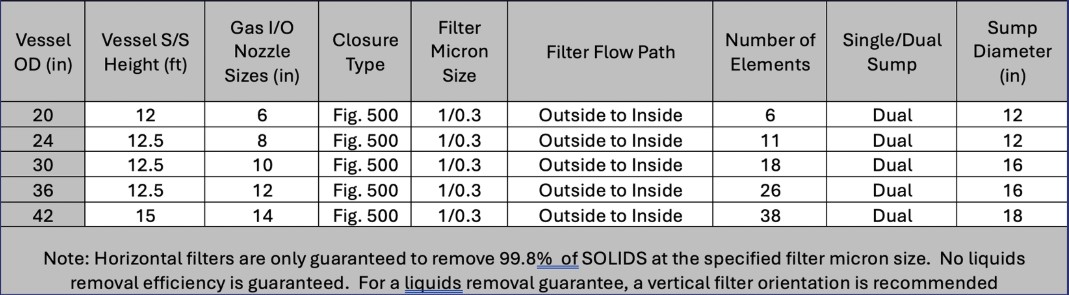
Horizontal and Vertical Filters
- Standard sizes up to 54”ID+, 200MMSCFD+
- Custom designs