The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for all industrial sectors of the U.S. economy. The rules are contained in 40 CFR 98 – Mandatory Greenhouse Gas Reporting. Facilities that have actual calendar year GHG emissions of 25,000 metric tons carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) must calculate and report GHG emissions to the EPA.
A total of 41 categories of reporters are covered by the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program.
Oil and Gas GHG Pollutants of Concern
The following are the GHG pollutants reported for oil and natural gas operations:
- Carbon dioxide: CO2
- Methane: CH4
- Nitrous oxide: N2O
Subpart C – General Stationary Fuel Combustion Sources
Subpart C applies to stationary fuel combustion sources (e.g., boilers, combustion turbines, engines, incinerators, and process heater) that emit 25,000 metric tons or more CO2e. The rule excludes flares (unless otherwise required by another subpart), portable equipment, emergency generators, emergency equipment and pilot lights
Subpart W – Petroleum and Natural Gas Systems
Subpart W applies to petroleum and natural gas systems that emit, in a calendar year, 25,000 metric tons or more CO2e. The sectors include:
- Onshore Production – report aggregated emissions from facilities within a Basin
- Offshore Production
- Gathering and Boosting – report aggregated emissions from facilities within a Basin
- Natural Gas Processing
- Natural Gas Transmission Compression
- Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline
- Underground Natural Gas Storage
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Import/Export
- LNG Storage. Liquefied Natural Gas storage equipment.
- Natural Gas Distribution
Combustion of fossil fuels from equipment are reported separately in Subpart C for all but Onshore Production and Gathering and Boosting sectors.
Many facilities do trigger mandatory reporting because their calendar year GHG emissions are below 25,000 metric tons CO2e/year.
Subpart PP – Suppliers of Carbon Dioxide
Subpart PP requires GHG reporting for suppliers of CO2 and includes the following facilities:
- Commercial applications that capture and maintain custody of a CO2 stream to sequester or inject it underground.
- Facilities with CO2 production wells.
- Importers of bulk CO2, if total combined imports exceed 25,000 metric tons of CO2e per year.
- Exporters of bulk CO2, if total combined exports exceed 25,000 metric tons CO2e per year
This source category does not include entities that store CO2 through geologic sequestration or above ground storage; use CO2 in enhanced oil and gas recovery; transport or distribute CO2; purify, compress, or process CO2; or import or export CO2 in equipment
Subpart RR – Geologic Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide
Subpart RR requires GHG reporting for facilities that inject CO2 underground for geologic sequestration.
Subpart UU—Injection of Carbon Dioxide
Subpart UU requires GHG reporting for facilities that inject CO2 underground for enhanced oil and gas recovery (EOR) or any other purpose other than geologic sequestration. Facilities that report under subpart RR for a well or group of wells are not required to report under subpart UU for that well or group of wells.
GHG Report Due Date
The GHG report must be submitted by March 31 each year. The report covers the GHG emissions from the previous calendar year. The online e-GGRT system is used to report GHG emissions.
e-GGRT System
The online system used to submit annual GHG reports is known as e-GGRT (Electronic Greenhouse Gas Reporting Tool).
The system requires users to setup accounts for the Designated Representative (DR) and Alternate Designated Representative (ADR). The DR and ADR can certify the GHG report. Agents (HSE inhouse staff and consultants) that prepare GHG reports need to setup an e-GGRT and be assigned to facilities by the DR or ADR.
The e-GGRT system has a useful Help section that includes Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) section. Also the e-GGRT system includes optional calculations spreadsheets that can be used for calculations.
Excel web forms for submitting reports for each applicable Subpart are supplied by e-GGRT. Also, e-GGRT has an XML reporting schema so facilities can upload GHG data directly in lieu of Excel web forms. Reporters must use the most current web form or XML schema.
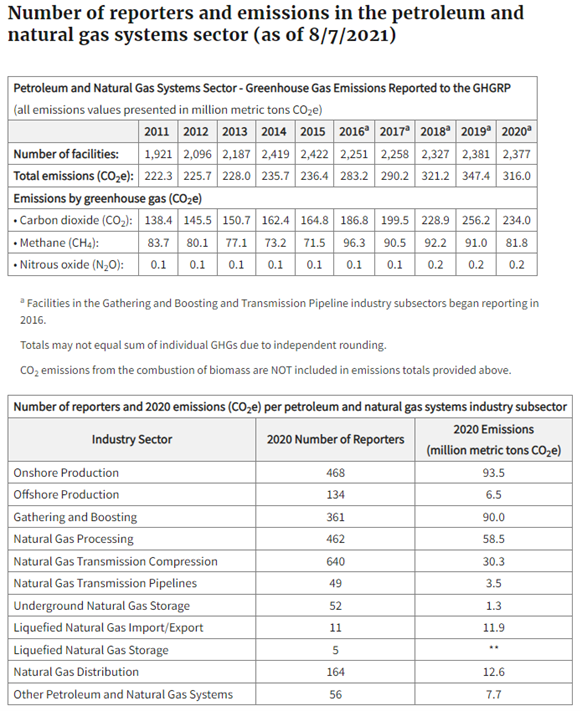
Recent summary data from the EPA’s website is shown below.
Ref: www.epa.gov/ghgreporting/ghgrp-petroleum-and-natural-gas-systems
Conclusions
The oil and natural gas industry has been reporting GHGs under the EPA mandatory reporting rule since 2011. There have not been any significant recent changes to the reporting rules in 40 CFR 98 that affect the oil and gas industry. Since the threshold for reporting is 25,000 metric tons CO2e per year, the EPA reported data does not include all possible GHG sources from petroleum and natural gas systems.
The reporting in 40 CFR 98 is separate from in-house GHG reports that companies prepare for ESG metrics, setting GHG reduction targets, shareholders and other purposes. Regardless of EPA GHG reporting requirements, all companies should consider calculating GHG emissions to determine if reporting has been triggered for their operations.
Cimarron – Who We Are
Cimarron can assist your company with equipment leak monitoring (LDAR) for Subpart W and NSPS OOOOa compliance. Our IQR team has experienced specialists that routinely conduct LDAR monitoring required by these regulations.
Cimarron’s overall goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions for all industries as we work with our clients to create a cleaner environment.
The company engineers and manufactures environmental, production and process equipment for the upstream, midstream and downstream energy industries, as well as environmental control solutions for biogas at wastewater facilities, digester tanks and landfills.
Cimarron offers our customers the know-how and environmental expertise to meet the environmental standards of today and tomorrow. Cimarron is committed to bring value to the Energy industry and their shareholders based on our financial strength, experienced personnel, and engineering capabilities.
As a company, we thrive every day to make a difference through innovation (e.g. ESG), customer focus, and operational efficiency. In addition to being present in all major regions in the US, Cimarron serves more than 45 countries around the world, ranging from offshore to desert. From key operational centers in the United States, Italy and the United Arab Emirates, Cimarron offers ongoing service and support through its own field service personnel and strategic third-party partners, creating a cleaner environment for our customers and their shareholders.
Since its founding in the mid-1970’s in Oklahoma, the company’s product offering has expanded from production equipment to include the largest line of environmental solutions that capture or incinerate fugitive vapors. With the acquisitions of HY-BON/EDI in 2019 and AEREON (including Jordan Technologies) in 2020, Cimarron has added strong brands, products, and services to its portfolio.
Please contact us to learn more about our products and services and about all our ESG solutions at sales@cimarron.com or visit our website cimarron.com.


